Micro-teaching is a teacher training technique designed to improve teaching practices in a structured and controlled environment. By allowing educators to focus on specific skills, it enables them to refine their methods while receiving constructive feedback. This blog dives into the essence of micro-teaching, its importance, and how to effectively use it, you can also read an in-depth analysis. We will also explore related concepts such as micro lesson plans, micro-teaching lesson plans, and the distinction between micro-teaching and macro-teaching.
What is Micro-Teaching?
At its core, micro-teaching refers to a scaled-down teaching exercise where educators present a brief lesson, typically lasting 5 to 10 minutes, to a small audience. This setup emphasizes improving particular teaching skills, making it an essential part of teacher training programs. Feedback from peers or supervisors plays a pivotal role, helping teachers reflect and grow.
Through micro-teaching, educators can master foundational skills like effective questioning, reinforcement, and clear communication, thus enhancing their overall teaching efficacy.
Why is Micro-Teaching Important?
Micro-teaching is a highly effective tool for teacher development, offering a focused, low-pressure environment where educators can refine specific skills. It allows teachers to concentrate on mastering individual techniques, such as using visual aids or framing effective questions, without the overwhelming demands of a full classroom. This focused approach helps teachers develop targeted competencies that are essential for effective teaching.
One of the key benefits of micro-teaching is the immediate, constructive feedback provided after each session. Educators receive actionable insights from peers or mentors, helping them identify strengths and areas for improvement. This feedback loop promotes continuous growth and allows teachers to make quick adjustments to their teaching methods.
Additionally, micro-teaching builds confidence by allowing repeated practice in a controlled setting. As educators rehearse techniques multiple times, they gain comfort and self-assurance, making them better prepared for real classroom challenges. This repetition helps teachers refine their skills and improve their overall teaching effectiveness.
By incorporating micro-teaching into training programs, institutions ensure that educators are well-prepared to handle diverse classroom scenarios. It bridges the gap between theory and practice, providing teachers with the tools and confidence needed to succeed in dynamic teaching environments.
What is a Micro Lesson Plan?
A micro lesson plan is a concise and focused version of a standard lesson plan. Unlike traditional lesson plans, it is designed for short teaching sessions and prioritizes precision and clarity.
Key components of a micro lesson plan include:
- Objective: Clear and measurable learning outcomes.
- Introduction: Engaging the audience with an attention-grabbing start.
- Content Delivery: Presenting the lesson in a concise and straightforward manner.
- Activity: Including an interactive exercise to solidify learning.
- Assessment: Quickly evaluate the understanding of the learners.
- Conclusion: Summarize the key points and address any lingering questions.
For example, a micro lesson plan on “effective questioning” might involve practicing open-ended questions with peers, followed by a brief analysis of their impact.
Crafting a Micro-Teaching Lesson Plan
A micro-teaching lesson plan is specifically designed to suit the goals of a micro-teaching session. It shares similarities with a micro lesson plan but emphasizes practicing specific skills under controlled conditions.
Steps to create an effective micro-teaching lesson plan:
- Identify the Skill: Decide on the teaching skill to focus on, such as explaining concepts or managing time effectively.
- Define Objectives: Clearly outline what you aim to achieve in the session.
- Organize Content: Plan a brief and engaging lesson centered on the chosen skill.
- Allocate Time Wisely: Ensure the lesson fits within a 5 to 10-minute timeframe.
- Include Feedback Mechanisms: Set aside time for receiving and reflecting on feedback from observers.
For instance, a micro-teaching lesson plan on “classroom management” could involve role-playing a disruptive scenario and practicing strategies to handle it effectively.
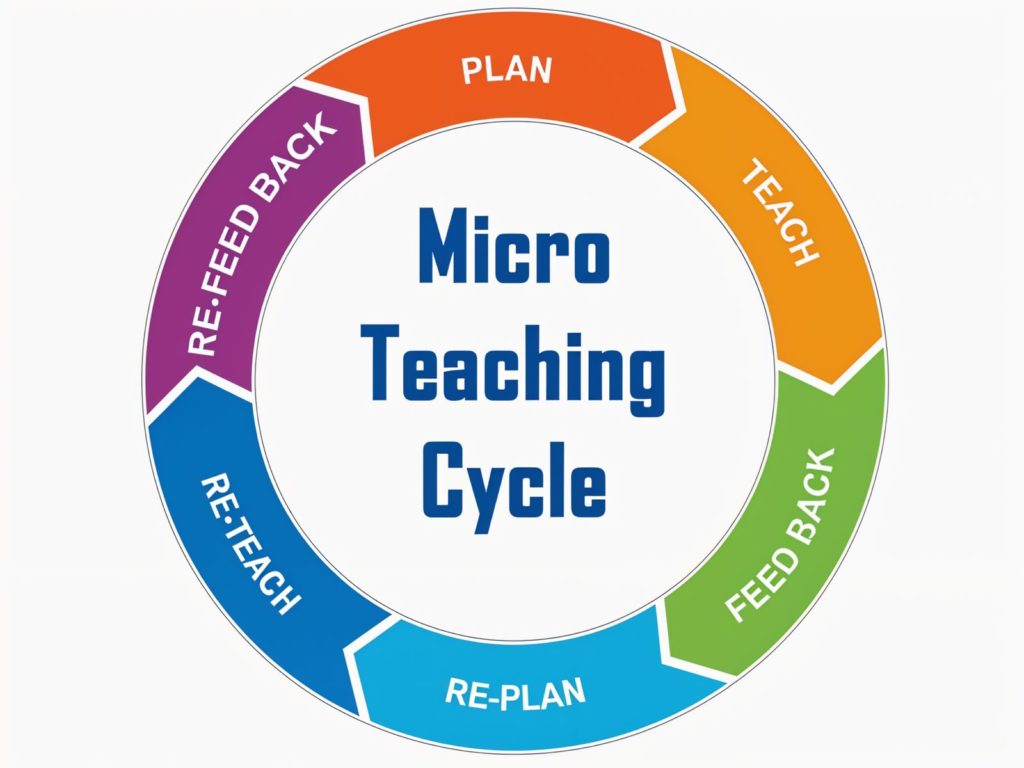
Steps of Micro-Teaching
The process of micro-teaching follows a systematic structure to maximize its effectiveness. Here’s how it works:
- Planning: The teacher prepares a concise lesson plan with a focus on a specific skill.
- Teaching: The lesson is delivered to a small group of peers or students.
- Feedback: Observers provide constructive feedback on the session.
- Reflection: The teacher reflects on the feedback to identify areas for improvement.
- Re-Teaching: A revised lesson is taught, incorporating the suggestions from the feedback.
- Evaluation: The overall effectiveness of the session is assessed.
This cyclical approach ensures continuous improvement and skill refinement.
Difference Between Micro-Teaching and Macro-Teaching
While both micro-teaching and macro-teaching aim to enhance teaching quality, they differ in scope and objectives:
- Micro-Teaching: Focuses on a specific skill or concept in a short session with a small group. It is ideal for training and practice.
- Macro-Teaching: Involves delivering the full curriculum to a larger audience over an extended period. It demands a broader set of skills and addresses diverse learner needs.
In essence, micro-teaching is a preparatory step that equips teachers with the confidence and skills needed for macro-teaching.
Why Are Micro-Teaching Skills Crucial?
Developing micro-teaching skills is essential for educators seeking to deliver impactful lessons. Key skills such as effective questioning, positive reinforcement, clear communication, classroom management, and non-verbal communication play a critical role in shaping a successful teaching experience. Effective questioning involves framing open-ended, thought-provoking questions that encourage deeper thinking and student participation. Positive reinforcement helps build a supportive learning environment, motivating students to engage and validating their efforts. Clear communication is crucial for explaining complex concepts in a way that is accessible and understandable, ensuring that all students can follow along. Classroom management skills, including maintaining discipline and fostering an inclusive, respectful environment, are necessary to ensure smooth lesson delivery and student engagement. Additionally, non-verbal communication—using gestures, facial expressions, and body language—enhances teacher-student interaction, making the lesson more engaging and dynamic. By honing these skills, educators can significantly improve their teaching effectiveness, creating an atmosphere that promotes active learning and student success. These micro-teaching skills help teachers build a strong foundation for creating more engaging, supportive, and effective learning experiences, ensuring that students are both motivated and capable of achieving their learning goals.
Practical Applications of Micro-Teaching
Micro-teaching is widely used in teacher training programs, professional development workshops, and even self-improvement initiatives. Some practical benefits include:
- Building confidence in novice teachers, how to build confidence in students?
- Allowing experimentation with new teaching techniques.
- Adapting to various classroom environments.
Educational institutions prioritize micro-teaching as it equips educators with the tools to succeed in dynamic teaching scenarios.
By embracing micro-teaching as a training tool, educators can enhance their teaching skills, boost their confidence, and prepare themselves for the dynamic challenges of real classrooms. With its structured approach and emphasis on feedback, micro-teaching ensures a practical and impactful learning experience for both teachers and students.
FAQs on Micro-Teaching
Q1: What is the main purpose of micro-teaching? The main purpose of micro-teaching is to help educators practice and refine specific teaching skills in a controlled and supportive environment.
Q2: How is a micro lesson plan different from a regular lesson plan? A micro lesson plan is shorter and focuses on one specific teaching objective, while a regular lesson plan addresses broader goals over a longer duration.
Q3: What are the steps involved in micro-teaching? The steps include planning, teaching, feedback, reflection, re-teaching, and evaluation.
Q4: How does micro-teaching compare to macro-teaching? Micro-teaching emphasizes skill refinement in small, focused sessions, whereas macro-teaching involves delivering comprehensive lessons to a larger audience.
Q5: Why is feedback essential in micro-teaching? Feedback provides educators with insights into their strengths and weaknesses, enabling them to make targeted improvements.
By embracing micro-teaching as a training tool, educators can enhance their teaching skills, boost their confidence, and prepare themselves for the dynamic challenges of real classrooms. With its structured approach and emphasis on feedback, micro-teaching ensures a practical and impactful learning experience for both teachers and students.





