The potential of online learning knows no bounds – with a few clicks, students from all corners of the globe can come together, exchanging ideas and knowledge across borders. A truly borderless classroom, where unique backgrounds, cultures and perspectives merge to create a kaleidoscope of colors, textures and dimensions in digital learning. However, online learning is more challenging for some learners than the others because of certain barriers to inclusive education in the online classroom!
Not all online learners have access to the same tools and terrain, facing roadblocks that threaten to derail their digital learning journeys. Whether slow networks, outdated devices or rigid formats that fail to flex with diverse needs, digital hurdles loom large.
As e-learning rises steadily in importance, what becomes of those left struggling? The risk of being lost in the fast lane of virtual education grows. We must unearth solutions! For only by understanding these “dividers” can we together forge a more inclusive online landscape – one representing each learner’s full potential and promise. Inclusive Education is where the online classroom unleashes, rather than limits, opportunity for all through accessible, adaptable and empowering design.
In this article, let us understand what is inclusive education, what are the various barriers to inclusive education that prevent students from achieving their learning objectives and how to overcome them.
What is Inclusive Education?
Inclusive Education can be defined as providing equal opportunities and support to all students, irrespective of their physical, intellectual, social, emotional, linguistic or other conditions. It aims to cater to the unique needs of each child through a system of flexible curricula, teaching methods and supports. Instead of segregating students with different abilities, inclusive classrooms embrace diversity by fostering an environment of learning and growth for every single student. The overall goal is to develop each child’s potential and skills to the maximum extent, so that they can learn, contribute and participate in the community meaningfully. When implemented successfully, inclusive education not only benefits students with special needs, but also creates a more compassionate society by teaching acceptance from a young age.
This is the vision of inclusive education, where every student feels welcome, supported, and challenged to reach their full potential. But what if some students face obstacles that hinder their ability to learn alongside their peers?
Interesting in teaching online through your own personalized app? Get in touch with experts at Classplus now to kickstart your online course business!
Also read – Digital Classrooms!
What are Barriers to Inclusive Education?
Barriers to inclusive education are obstacles that prevent students from fully participating and reaching their potential in a general classroom setting. These can be physical limitations like inaccessible buildings, or challenges related to learning styles, where a one-size-fits-all approach doesn’t cater to individual needs. Curriculums that lack flexibility or don’t consider diverse learning paces can also hinder progress. Negative attitudes, unconscious biases, or a lack of qualified support staff can create a sense of exclusion. Financial constraints can limit access to resources and adaptations, while cultural or language barriers might make it difficult for some students and their families to feel fully connected to the school community.
Types of Barriers to Inclusive Education
Creating a truly inclusive classroom where all students thrive, learn and feel like they belong, requires addressing various challenges. Let’s break down some of the most common roadblocks that hamper student learning below –
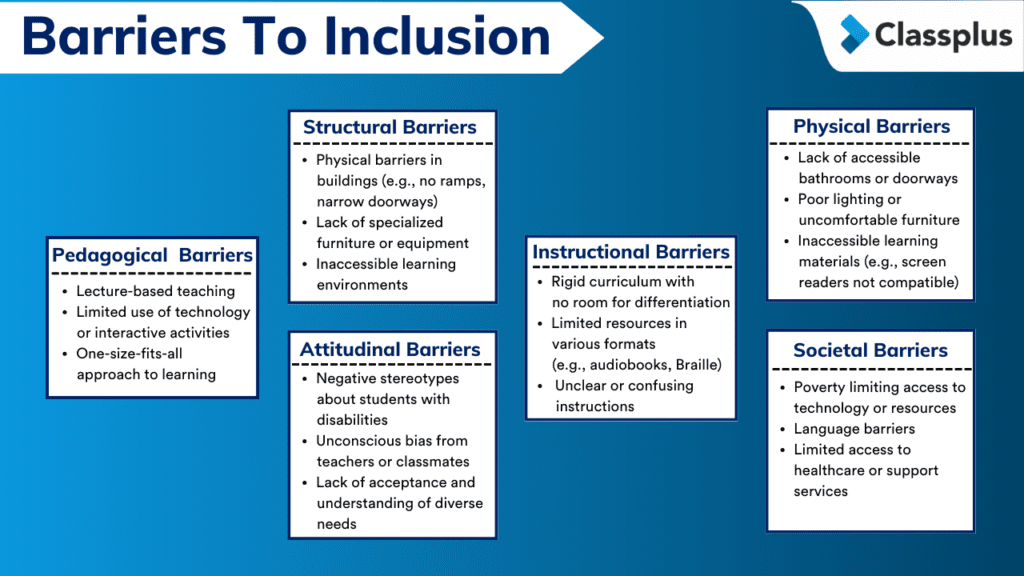
Pedagogical Barriers to Inclusive Education
Pedagogical barriers to inclusive education focus on teaching methods that might not cater to diverse learning styles. Imagine a teacher relying solely on lectures for a class with students who learn best by doing hands-on activities or working visually. This approach can leave some students behind. Inclusive pedagogy involves using a variety of teaching methods and assessments to ensure all students have a chance to excel.
One example of pedagogical barriers can be Traditional Lectures translated directly to online video presentations. This can leave students with kinesthetic or visual learning styles disengaged and the students who learn best through hands-on activities might struggle to grasp the concepts.
Structural Barriers to Inclusive Education
These are physical limitations in the learning environment. Think about a school building without ramps or elevators, making it inaccessible for students with mobility impairments. Structural barriers can also include a lack of appropriate furniture or specialized equipment to support students with various needs. For example, a student living in a rural area with poor internet connectivity will struggle to participate in live online sessions.
To remedy this,
- Offer asynchronous learning options!
- Record lectures and make them available for later viewing.
- Provide downloadable course materials for offline access.
- Explore alternative learning methods like printed workbooks or project-based activities that can be completed offline.
Attitudinal Barriers to Inclusive Education
These stem from negative stereotypes or unconscious bias. A teacher who believes students with disabilities can’t achieve high academic standards is creating an attitudinal barrier. Similarly, classmates who make fun of someone who learns differently can create a hostile environment. Inclusive classrooms require a shift in mindset, fostering acceptance and celebrating diversity. Negative stereotypes can persist online as well. For instance, a teacher assuming students with ADHD can’t focus during asynchronous lectures creates a barrier.
As an online educator, you must foster a positive online community! Set clear expectations for online interactions, encourage respectful communication, and offer alternative ways for students to participate, like written assignments or breakout room discussions.
Instructional Barriers to Inclusive Education
These barriers relate to the way content is presented in the classroom. Is the curriculum too rigid, offering little opportunity for differentiation based on individual needs? Are there limited resources available in different formats, like audiobooks for struggling readers? Instructional materials that are not adapted for diverse learners can create obstacles to participation. For example, an online course that only offers text-based materials. Students with visual impairments who rely on screen readers might find the content inaccessible.
Physical Barriers to Inclusive Education
These encompass any limitations that hinder a student’s ability to physically access or participate in the classroom. This could be a lack of accessible bathrooms, narrow doorways, or poorly lit classrooms that strain students’ eyesight. Educators need to ensure their physical environment is welcoming and accessible for all learners. A student with vision impairments might find the online interface difficult to navigate due to lack of keyboard shortcuts or screen reader compatibility.
| Pro Tip! Use features like screen readers, closed captions, and keyboard navigation options to make your online classroom accessible for learners with vision impairments. |
Societal Barriers to Inclusive Education
These are social barriers which stem from broader social issues that impact education. Poverty, limited access to healthcare, or language barriers can all create challenges for students. Social issues like poverty or limited access to technology can create an uneven playing field for online learning. For instance, a student from a low-income family doesn’t have a reliable device to access online lessons. Schools can’t solve these issues alone, but they can be aware of these societal barriers and work to bridge the gap by providing additional support and resources.
“Digital Divide” – Barriers to Inclusive Online Learning
While online learning has helped with continued education, it has also aggravated existing inequities. Not all students have access to computers and reliable internet. Imagine zooming in to a class and right when the teacher is explaining key concepts, the Internet cuts out! Online learning is not a level playing field. With unequal access to technology, it is rather a “digital cliff” where certain learners might face more challenges than others.
| Did You Know? According to UNICEF, 46% of the world’s population is not online. |
Those with disabilities also face unique challenges with inaccessible content, lack of personalized support and assistive technology not working well in online settings. Students from low-income families and remote areas are disproportionately impacted due to the lack of resources. Engaging all learners equally is difficult without face-to-face interaction. Those with language barriers or special needs tend to struggle with self-paced learning in the absence of guidance.
Common Barriers to Inclusive Online Education
Some key factors that impede inclusive online education include –
- socioeconomic inequalities
- limitations of virtual learning for certain disabilities
- inadequate technical support and training for using edtech tools
- paucity of individualized accommodations
- engagement difficulties for those in remote areas
- lack of peer interaction
- language and cultural challenges for linguistic minorities
- inadequate cyber-safety measures.
With online modes becoming mainstream, it is important that all efforts are made to remove barriers like the digital divide, lack of content accessibility, inability to accommodate diverse needs and ensure no child is left behind in their right to learn.
Check some Inclusive Learning Strategies to engage all students productively!
Overcoming Barriers of Inclusive Education
Every student deserves a shot at learning. By removing barriers to inclusive learning, we open doors for all, creating a stronger, more successful classroom for everyone. This isn’t just about fancy tech or trendy platforms – it’s about making sure every learner, regardless of background, has a fair shot at a quality education. Online learning should not be just a privilege, but a powerful tool for inclusive education that empowers everyone to reach their full potential. Let us look at some of the ways to overcome barriers to inclusive education below –
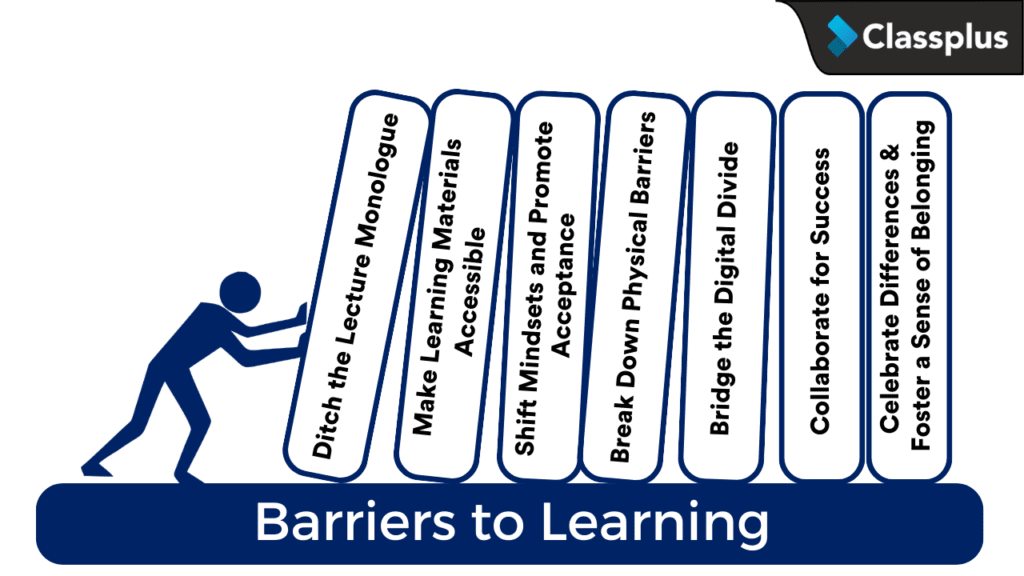
1. Ditch the Lecture Monologue
Remember – One Size Doesn’t Fit All. Not everyone learns best by listening to a teacher talk for an hour. Introduce a variety of teaching styles. Incorporate interactive activities that get students moving and thinking critically. Think science experiments, debates on historical events, or collaborative art projects.
Encourage group discussions where students can learn from and teach each other. For online learning, explore breakout rooms for small group discussions, quizzes to gauge understanding, and collaborative whiteboards for brainstorming sessions.
Consider offering students the option to create a short video presentation as an alternative assignment, allowing them to showcase their learning in a way that suits their strengths.
2. Make Learning Materials Accessible
Ditch only text-based resources! Provide materials in various formats to cater to diverse learning styles and overcome challenges.
- Offer audiobooks for students who struggle with reading or prefer auditory learning.
- Create captioned videos for students who are deaf or hard of hearing.
- Use dyslexia-friendly fonts and offer downloadable PDFs with text-to-speech options for students with dyslexia.
- Explore screen readers and other assistive technologies to ensure everyone can access the information they need.
Online Educators can work with specialists to identify and implement appropriate learning materials for students with visual impairments, such as tactile diagrams or braille versions of key texts.
3. Shift Mindsets and Promote Acceptance
Challenge Stereotypes and Build a Culture of Respect. Unconscious bias can hinder inclusion. Hold workshops and discussions to explore unconscious bias and its impact on the learning environment. Create a classroom culture that celebrates diversity and fosters empathy. Encourage students to learn about different cultures, backgrounds, and abilities through literature, guest speakers, and classroom projects. Address any instances of prejudice head-on, promoting respectful communication and creating a safe space for all students to voice their opinions and experiences.
4. Break Down Physical Barriers
Is Your Classroom Accessible? This goes beyond ramps and wide doorways. Think about ensuring accessible furniture with adjustable heights for students who use wheelchairs or have difficulty reaching desks. Clear pathways are essential, as are grab bars in bathrooms. For online learning environments, consider the accessibility of the chosen platform. Does it offer features like closed captions for video lectures and keyboard shortcuts for easy navigation? Partner with accessibility specialists to test the online platform and identify potential roadblocks for students with physical limitations.
5. Bridge the Digital Divide
Connect Learners in the Digital World. While loaner devices and internet hotspots can be a great solution, consider the ongoing costs and potential limitations. Explore partnerships with local libraries or community centers that offer free computer access and internet connectivity. For students in remote areas with limited internet options, consider providing learning materials on USB drives or even printed copies.
Think creatively about alternative learning activities for offline use, such as downloadable workbooks with hands-on projects or self-paced study guides. For online learning platforms, ensure downloadable course materials are available in various formats for offline access.
6. Collaborate for Success
Open communication is crucial. Regular meetings or online forums can help teachers, parents, and specialists share insights and develop a holistic understanding of each student’s needs. Parents can provide valuable information about their child’s learning style and any specific accommodations needed. Specialists, such as occupational therapists or speech-language pathologists, can offer guidance and support strategies. In online learning environments, utilize online collaboration tools for communication between teachers, parents, and students. Explore features like video conferencing for virtual meetings and online forums for ongoing discussions.
7. Celebrate Differences & Foster a Sense of Belonging
Every Student Matters! Integrate cultural celebrations and activities into the curriculum, both online and in physical classrooms. For online learning, encourage students to share presentations about their cultural heritage or traditions. Create virtual bulletin boards or online discussion forums where students can showcase their artwork, music, or writing inspired by their backgrounds. In physical classrooms, create a welcoming environment with displays that celebrate diversity. Encourage students to learn about different cultures through online guest speakers, virtual field trips to museums or historical sites, and collaborative projects that explore diverse perspectives.
Know How to Engage Students in Special Education Classrooms!
Let’s Sum It Up!
While online learning has increased access to education during the pandemic, it has also exposed the deep digital and accessibility divides that hinder inclusive learning. The digital divide has become a glaring obstacle, leaving some students stuck on the wrong side of a walled garden.
If left unaddressed, these divides risk marginalizing the most vulnerable student populations and exacerbating existing inequities. It is imperative for governments and educational institutions to focus on bridging technology gaps, ensuring online content is inclusive for all, and providing adequate learner support to make certain no child is excluded from continuing their education. Only by removing barriers facing students from disadvantaged sections can we truly achieve the vision of an equitable and inclusive digital education system for all.
Barriers to Inclusive Education FAQs
Some of the biggest barriers of inclusive education include – lack of adequate training for teachers, inaccessible school facilities and lack of funding to support inclusion efforts. Attitudinal barriers stemming from social stigmas also negatively impact children with diverse needs.
Barriers can be overcome through collaborative efforts from all stakeholders. This includes improving awareness, providing reasonable accommodations, investing in teacher training, introducing flexible curriculums and securing committed funding to meet individualized needs of all students.
Barriers include lack of resources, large classes, outdated teaching methods, inadequate teacher training, inaccessible facilities, rigid curriculums, social stigmas, and insufficient community support, all hindering effective learning.
Barriers include the digital divide, limitations for disabilities, usability issues with assistive tools, lack of personalized learning options, engagement problems, language/cultural barriers, and tech literacy challenges for students and parents.
Online learning can be made more accessible by enhancing access with devices and internet, personalizing learning, ensuring compatibility with assistive tools, encouraging peer support, using diverse learning modes, accommodating different learning styles, fostering an inclusive culture, and providing effective communication and support mechanisms for all learners.



